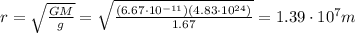We can solve the problem in two steps:
1) From the weight W=50.0 N of the object, we can find the value of the gravitational acceleration g of the planet. In fact, the weight is equal to
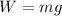
where m=30 kg is the mass of the object. From this, we find g:
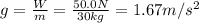
2) The gravitational acceleration of a planet with mass M and radius r is given by
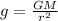
where
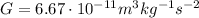
is the gravitational constant. In our problem, the mass of the planet is
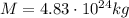
, and we found g in step 1),
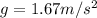
, so we have everything to solve and find the value of the radius r: