Answer: The atomic number of the atom is the number of electrons in the atom only when the atom is neutral.
Step-by-step explanation: For a neutral atom, the number of positive charges is equal to the number of negative charges and thus the atomic number is equal to the number of electrons or the number of protons.
But for a positive and a negative ion, the electrons are lost and gained respectively by that element and thus the number of electrons are not equal to the number of protons. Now atomic number is equal to the number of protons only. The number of electrons = number of protons - charge.
Example: For sodium
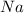 , the atomic number is 11 and it has 11 electrons.
, the atomic number is 11 and it has 11 electrons.
For sodium ion
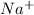 , the atomic number is 11 but the number of electrons = (11-1) = 10.
, the atomic number is 11 but the number of electrons = (11-1) = 10.