Answer:
C. A quantity with magnitude and a direction.
Step-by-step explanation:
A vector can be defined as a quantity with magnitude and direction. Some examples of vector quantities are velocity, position, displacement, force, torque, acceleration.
For example, given the following data;
Time, t = 18.5secs
Final velocity = 78m/s
Initial velocity = 0
Substituting into the equation;
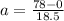
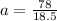
Acceleration, a = 4.22m/s²
Therefore, the acceleration of the object is 4.22m/s² due North.
In physics, acceleration can be defined as the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time.
This simply means that, acceleration is given by the subtraction of initial velocity from the final velocity all over time.
Hence, if we subtract the initial velocity from the final velocity and divide that by the time, we can calculate an object’s acceleration.
Mathematically, acceleration is given by the equation;
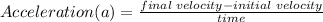
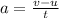
Where,
a is acceleration measured in
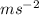
v and u is final and initial velocity respectively, measured in
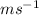
t is time measured in seconds.