Qualitatively the momentum is the amount of motion contained in the body.
Quantitatively momentum is the product of mass and velocity of the body.
Mathematically momentum= mass×velocity
i.e p=m×v
where p denotes the momentum.
As per the question the initial velocity of the particle is given as [u]=60 m/s
The final velocity of the particle is given as [v]=30 m/s
Let the mass of the particle is m kg
The initial momentum
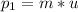
=60m kg m/s
the final momentum
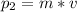
=30m kg m/s
Hence the change in momentum is given as -
![p_(2) -p_(1) =[30m -60m] kg m/s](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/middle-school/jn5tijri9v4ykgjbvy4ayzy6n1mvbyp1p4.png)
= -30m kg m/s
Here the minus sign indicates the loss of momentum
Hence the momentum is decreased by twice as the velocity is decreased by twice.
In general if velocity is decreased by m times ,then the momentum is decreased by m times also.