The answer is the following:
"what occurs with Doppler effect are changes in frequency due to motion"
The Doppler effect occurs when the source of a wave and the observer are moving relative to each other. Due to this fact, the observer will see the wave moving at a different velocity v' with respect to the real velocity of the wave as emited by the source. As a consequence, the frequency of the wave as seen by the observer is shifted, according to the following relationship:
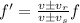
where:
f' is the apparent frequency, as seen by the observer
f is the real frequency
v is the velocity of the wave
vr is the velocity of the observer relative to the source of the wave (it is positive if the observer is moving towards the source, negative if he is moving away)
vs is the velocity of the source relative to the observer (it is positive if the source is moving away from the observer, negative if it is moving towards him)