If we are assuming ideal behavior, then the Ideal Gas Equation,
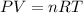
, is very helpful. The number of moles
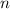
changes here by a factor of
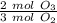
, so you have
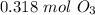
.
So,
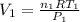
and
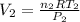
. Looking at the given information, P and T are constant (as is R, always). So, we can write
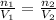
. Solving for
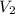
, we get
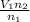
. Then we plug in 12.1 L for
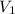
,
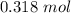
for
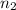
and
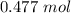
for
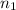
. Thus
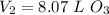
.