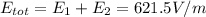The electric field generated by an infinite plane uniformly charged is
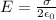
where
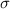
is the charge density of the plane, while
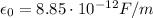
is the vacuum permittivity.
Let's calculate the electric field of the first (xy) plane:
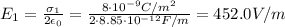
And now the electric field due to the second (z=2.0 m) plane:
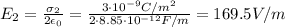
The electric field of the two planes does not depend on the distance. Also, the charges on the two planes have same sign, so at z=3.0 m (and at every point with z>2.0m) the two fields point into the same direction and the total electric field is simply the sum of the two fields: