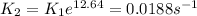Missing details. Complete text is:
"The following reaction has an activation energy of 262 kJ/mol.
C4H8(g) --> 2C2h4(g)
At 600.0 K the rate constant is 6.1× 10–8 s–1. What is the value of the rate constant at 790.0 K?"
To solve the exercise, we can use Arrhenius equation:
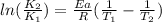
where K are the reaction rates, Ea is the activation energy, R=8.314 J/mol*K and T are the temperatures. Using
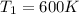 and
and
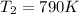 , and Ea=262 kJ/mol = 262000 J/mol, on the right side of the equation we have
, and Ea=262 kJ/mol = 262000 J/mol, on the right side of the equation we have
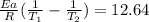
And so
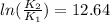
And using
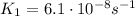 , we find K2:
, we find K2: