The magnetic force (Lorentz force) experienced by the proton in the magnetic field is given by
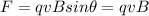
since
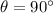
, because the velocity v and the force F in this problem are perpendicular, and so also the angle
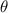
between the velocity and the magnetic field B should be
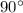
.
Let's find the magnitude of the magnetic field; this is given by
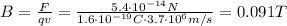
To understand the direction, let's use the right-hand rule:
-index finger: velocity
- middle finger: magnetic field
- thumb: force
Since the velocity (index) points east and the force (thumb) points south, then the magnetic field (middle finger) points downwards. So we write:
B = -0.091 T