Answer: The correct statement is the larger the standard reduction potential, the more likely the half-reaction will occur as a reduction.
Step-by-step explanation:
Standard reduction potential is defined as the tendency of a chemical species to get reduced. This is measured in volts at standard conditions.
If the specie has negative reduction potential, it means that it will easily loose electrons and thus, will get oxidized.
Similarly, if the species has positive reduction potential, it means that it will easily gain electrons and thus, will be reduced.
For Example: The reduction potentials of
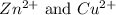 are given as:
are given as:
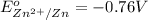
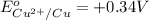
The copper ion will get easily reduced as compared to zinc ion.
Hence, the correct statement is the larger the standard reduction potential, the more likely the half-reaction will occur as a reduction.