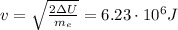Incomplete question. The complete text is (found on internet)
"Consider two points in an electric field. The potential at point 1, V1, is 46 V. The potential at point 2, V2, is 157 V. An electron at rest at point 1 is accelerated by the electric field to point 2.
(a) write an equation for the change of electric potential energy change of U of the electron in terms of the symbols given.
(b) find the numerical value of the change of the electric potential energy in electron volts (eV)
(c) express v2, the speed of the electron at point 2, in terms of change in U, and the mass of the electron me
(d) find the numerical value of v2 in m/s"
(a) Calling
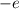 the electron charge, the variation of the electric potential energy is:
the electron charge, the variation of the electric potential energy is:
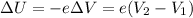
(b) Using the value of e, and of V1 and V2, we can calculate the variation of electric potential energy of the electron going from point 1 to point 2:
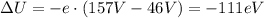
(c) The electron lost -111 eV of electric potential energy moving from point 1 to point 2. This energy has converted into kinetic energy:
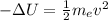
where v is the electron velocity in point 2 and me is the electron mass. So we can write v as
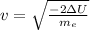
(d) and then, we can calculate the value of the electron velocity. First we have to convert
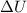 from eV to joule:
from eV to joule:
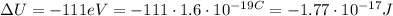
So, using the electron mass
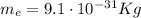 , we have:
, we have: