Answer: 448 g of
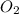 will be required to completely react with 784g moles of CO(g) during this reaction.
will be required to completely react with 784g moles of CO(g) during this reaction.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the moles :
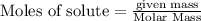
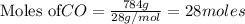
The balanced chemical equation is:
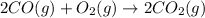
According to stoichiometry :
2 moles of
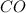 require = 1 mole of
require = 1 mole of
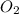
Thus 28 moles of
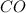 will require=
will require=
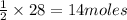 of
of
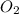
Mass of
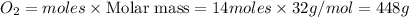
Thus 448g of
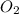 will be required to completely react with 784g moles of CO(g) during this reaction.
will be required to completely react with 784g moles of CO(g) during this reaction.