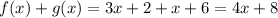
. This function is defined for all real numbers.

. This function is also defined for all real numbers.
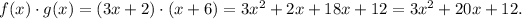
As before, this function is defined for all real numbers

.
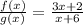
. Fractions are undefined when their denominators are zero, so if
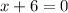
, this function is undefined. Thus, the domain is all real numbers except

.