Answer:
v = 0.54 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The Principle Of Conservation Of Mechanical Energy
In the absence of friction, the total mechanical energy is conserved. That means that
Em=U+K is constant, being U the potential energy and K the kinetic energy
U=mgh
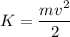
When the mass (m=1 kg) of the pendulum is at the top of the path at a height of h=1.5 cm=0.015 m, its kinetic energy is 0 and its potential energy is:
U=1 * 9.8 * 0.015 = 0.147 J
That potential energy is completely transformed into kinetic energy at the bottom of the swing. The speed can be calculated by solving for v:
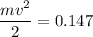
Multiplying by 2 and dividing by m:
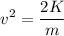
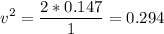
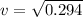
v = 0.54 m/s