Answer:
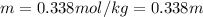
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, since the molality is defined in terms of the moles of solute divided by the kilograms of solvent as shown below:
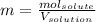
One firstly computed the moles of glucose which acts as the solute as follows:
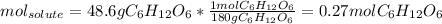
Now, as the density of water is 1.00 g/mL, we conclude we have 0.8 kg of water, therefore, the resulting molality in molar units (m) turns out:
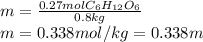
Best regards.