Answer:
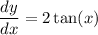
General Formulas and Concepts:
Calculus
Differentiation
- Derivatives
- Derivative Notation
Derivative Property [Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [cf(x)] = c \cdot f'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/high-school/h3h81fknzks3m5lkzvmdwrmpof8mpsbacs.png)
Derivative Rule [Chain Rule]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[f(g(x))] =f'(g(x)) \cdot g'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ijuuby0owovgvvmkyt63pxr8cpkn8j9mgp.png)
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
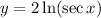
Step 2: Differentiate
- Logarithmic Differentiation [Chain Rule, Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle (dy)/(dx) = 2 \bigg( (1)/(\sec x) \bigg) \cdot (d)/(dx)[\sec x]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/college/cgkwrdemiwyf2a7o2qef1nzjju030kt7bq.png)
- Trigonometric Differentiation:
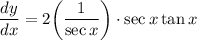
- Simplify:
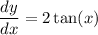
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Differentiation