Answer:
750.8 grams of CaCO₃ are present in a sample if there are 4.52*10²⁴ atoms of carbon in that sample.
Step-by-step explanation:
Avogadro's Number or Avogadro's Constant is called the number of particles that make up a substance (usually atoms or molecules) and that can be found in the amount of one mole of said substance. Its value is 6.023 * 10²³ particles per mole. The Avogadro number applies to any substance.
So, the following rule of three applies: if 6.02 * 10²³ carbon atoms are contained in 1 mole of said compound, 4.52*10²⁴ atoms in how many moles will they be contained?
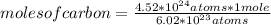
moles of carbon=7.508
For the given compound, you can see that one mole of CaCO₃ contains one mole of carbon. This means that 7,508 moles of carbon will be present in 7,508 moles of CaCO₃.
To know the mass you must know the molar mass of the compound. You know what:
- Ca: 40 g/mole
- C: 12 g/mole
- O: 16 g/mole
So: CaCO₃= 40 g/mole + 12 g/mole + 3*16 g/mole= 100 g/mole
So, you apply a rule of three as follows: if one mole of the compound contains 100 g, 7,508 moles of CaCO₃, how much mass will it contain?
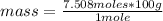
mass= 750.8 grams
750.8 grams of CaCO₃ are present in a sample if there are 4.52*10²⁴ atoms of carbon in that sample.