The probability is
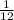 .
.
To find the probability of rolling an even number on the first die and a number greater than 5 on the second die, we can consider the possible outcomes.
A standard six-sided die has the numbers 1 through 6.
Even number on the first roll: The even numbers on a die are 2, 4, and 6. So, there are 3 favorable outcomes.
Number greater than 5 on the second roll: The numbers greater than 5 on a die are 6. So, there is 1 favorable outcome.
Now, multiply the number of favorable outcomes for each roll:
P(Even on the first roll and >5 on the second roll)=P(Even on the first roll)×P(>5 on the second roll)
P(Even on the first roll and >5 on the second roll)=
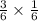
Simplify the expression:
P(Even on the first roll and >5 on the second roll)=
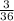
Reduce the fraction:
P(Even on the first roll and >5 on the second roll)=
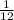
So, the probability is
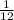 .
.