Answer: The specific gravity of glucose solution is 1.02
Step-by-step explanation:
The relationship between specific gravity and density of a substance is given as:
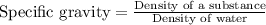
We are given:
Density of glucose solution = 1.02 g/mL
Density of water = 1.00 g/mL
Putting values in above equation we get:
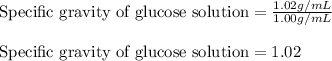
Hence, the specific gravity of glucose solution is 1.02