Answer: The moles of argon gas contained in the cylinder is 106.32 mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles of gas, we use the equation given by Ideal gas, which is:
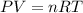
where,
P = pressure of the gas = 10130 kPa
V = Volume of the gas = 50 L
n = Number of moles of gas = ? moles
R = Gas constant =
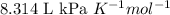
T = Temperature of the gas = 300° C = 573 K (Conversion factor:
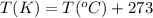
Putting values in above equation, we get:
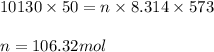
Hence, the moles of argon gas contained in the cylinder is 106.32 mol.