Answer:
The total number of moles of reactants consumed when 1.00 mole of CO₂ (g) is produced is 2 moles.
Step-by-step explanation:
You have that the balanced reaction is:
C₃H₈ (g) + 5 O₂ (g) ⇒ 3 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂O (l)
By stoichiometry of the reaction (that is, the relationship between the amount of reagents and products in a chemical reaction), the following amounts of reactants and products participate in the reaction:
- C₃H₈: 1 mole
- O₂: 5 moles
- CO₂: 3 moles
- H₂O: 4 moles
The rule of three or is a way of solving problems of proportionality between three known values and an unknown value, establishing a relationship of proportionality between all of them.
If the relationship between the magnitudes is direct, that is, when one magnitude increases, so does the other (or when one magnitude decreases, so does the other) , the direct rule of three must be applied. To solve a direct rule of three, the following formula must be followed:
a ⇒ b
c ⇒ x
So
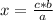
where a, b and c are known values. In this case the rule of three is applied as follows: if by stoichiometry of the reaction 3 moles of CO₂ consume 1 mole of C₃H₈, then 1 mole of CO₂ how many moles of C₃H₈ will it consume?
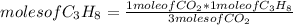
moles of C₃H₈= 0.33
Applying again a new rule of three: if by stoichiometry of the reaction 3 moles of CO₂ consume 5 moles of O₂, then 1 mole of CO₂ how many moles of O₂ will it consume?
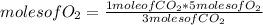
moles of O₂=1.67
The total number of moles of reactants consumed will be the sum of the consumed moles of C₃H₈ and the consumed moles of O₂:
0.33 moles + 1.67 moles=2 moles
The total number of moles of reactants consumed when 1.00 mole of CO₂ (g) is produced is 2 moles.