Answer:
when gravity equals air resistance
Step-by-step explanation:
There are two forces acting on a skydiver falling down:
1) Gravity - this force acts downward, and it is constant during the whole fall, because its magnitude is given by
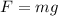
where m is the mass of the skydiver and g the gravitational acceleration. Both quantities are constant, so the force of gravity is constant.
2) Air resistance - this force acts upward, and it is not constant: it is proportional to the velocity of the skydiver
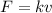
where k is a constant and v is the velocity. Therefore, as the skydiver falls down, its velocity increases and the air resistance increases as well.
The equation of forces for the skydiver is therefore:
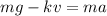
where a is the skydiver's acceleration. At the beginning of the fall,
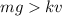 , so the skydiver accelerates towards the ground. However, as he accelerates, the air resistance
, so the skydiver accelerates towards the ground. However, as he accelerates, the air resistance
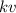 increases, till the moment at which air resistance becomes equal to gravity:
increases, till the moment at which air resistance becomes equal to gravity:
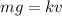
when this condition occurs, then the acceleration becomes zero, so the skydiver no longer accelerates and continues his fall at constant speed. This constant speed is called terminal velocity, and so it occurs when
gravity equals air resistance