Answer: 0.422 M⁻¹s⁻¹
Step-by-step explanation: Reaction Rate is the speed of decomposition of the reactant(s) per unit of time.
A Rate Law relates concentration of reactants, rate reaction and rate constant:
![r=k[A]^(x)[B]^(y)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/ru54pd59sv84truh6ndu3wgx3e61f7ev1a.png)
where
[A] and [B] are reactants concentration
x and y are reaction order, not related to the stoichiometric coefficients
k is rate constant
r is rate
Before calculating rate constant, first we have to determine reaction order.
In this question, the reactio order is 2. So, the rate law for it is
![-(d[A])/(dt) =k[A]^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/7g0eq4cybh9f4m6q05obxs8eghz45ingdx.png)
and the integrated formula is
![(1)/([A]) =(1)/([A]_(0)) +kt](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/m7s6pvyr76mynpnjw95bcz9qlcsyu7qbjn.png)
in which
[A]₀ is initial concentration of reactant
Then, using initial concentration at initial time and final concentration at final time:
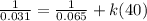
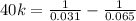
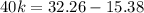
k = 0.422
The rate constant for the reaction is 0.422 M⁻¹.s⁻¹