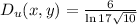Answer:
The directional derivate is given by:
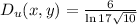
Explanation:
The directional derivative at point (x,y) is given by:
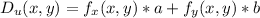
In which a is the x component of the unit vector and b is the y component of the unit vector.
Vector:
We are given the following vector:
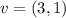
Its modulus is given by:
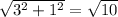
The unit vector is given by each component divided by it's modulus. So
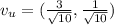
This means that
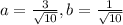
Partial derivatives:
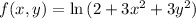
So
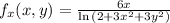
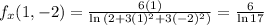
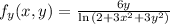
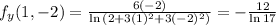
Directional derivative:
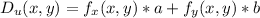
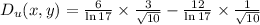
![D_(u)(x,y) = (18)/(ln(17)√(10)) - (12)/(ln(17)√(10))[tex]</p><p>[tex]D_(u)(x,y) = (6)/(ln(17)√(10))](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/5drv34mnlgb4shi0i321cwv2v81kqv0c58.png)
The directional derivate is given by: