Answer:
a)
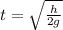
b) Ball 1 has a greater speed than ball 2 when they are passing.
c) The height is the same for both balls = 3h/4.
Step-by-step explanation:
a) We can find the time when the two balls meet by equating the distances as follows:
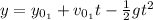
Where:
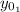 : is the initial height = h
: is the initial height = h
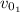 : is the initial speed of ball 1 = 0 (it is dropped from rest)
: is the initial speed of ball 1 = 0 (it is dropped from rest)
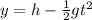 (1)
(1)
Now, for ball 2 we have:
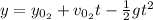
Where:
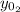 : is the initial height of ball 2 = 0
: is the initial height of ball 2 = 0
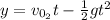 (2)
(2)
By equating equation (1) and (2) we have:
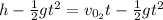
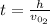
Where the initial velocity of the ball 2 is:
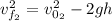
Since
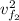 = 0 at the maximum height (h):
= 0 at the maximum height (h):
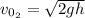
Hence, the time when they pass each other is:
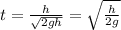
b) When they are passing the speed of each one is:
For ball 1:
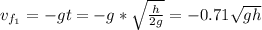
The minus sign is because ball 1 is going down.
For ball 2:
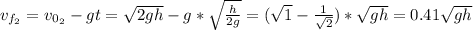
Therefore, taking the magnitude of ball 1 we can see that it has a greater speed than ball 2 when they are passing.
c) The height of the ball is:
For ball 1:
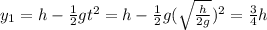
For ball 2:
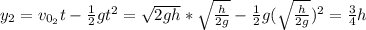
Then, when they are passing the height is the same for both = 3h/4.
I hope it helps you!