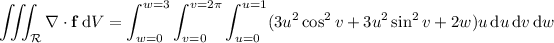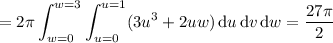Since the region is closed, we can apply the divergence theorem.
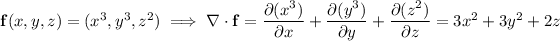
The divergence theorem states that the flux of
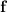
across a surface
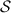
enclosing a region
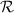
is equivalent to the volume integral of
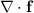
(the divergence of
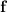
over
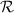
:
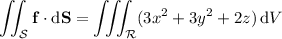
To compute the integral, we convert to cylindrical coordinates using
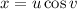
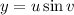
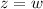
so that
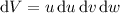
. Now the integral becomes