Answer: The correct match is given below.
Step-by-step explanation: We know that the type of angled triangle can be found out by the following method:
if sum of the squares of two sides of shortest lengths > Square of length the greatest side ⇒ it is an acute angled triangle
if sum of the squares of two sides of shortest lengths = Square of length the greatest side ⇒ it is a right angled triangle
if sum of the squares of two sides of shortest lengths < Square of length the greatest side ⇒ it is an obtuse angled-triangle.
Also, if all the sides of the triangle are equal in length, then the triangle is equilateral.
if two sides of the triangle are equal in length, then the triangle is isosceles.
if none of the sides of the triangle are equal in length, then the triangle is scalene.
For the first trianlge: A(2, 0), B(3, 2), C(5, 1).
We have
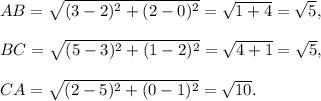
Since AB = BC and AB² + BC² = CA², so the triangle is isosceles right-angled triangle.
For the second trianlge: A(4, 2), B(6, 2), C(5, 3.73).
We have
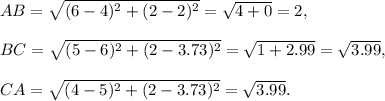
Since BC = CA and BC² + CA² > CA², so the triangle is isosceles acute angled triangle.
For the third trianlge: A(-5, 2), B(-4, 4), C(-2, 2).
We have
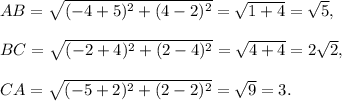
Since AB ≠ BC ≠ CA and AB² + BC² > CA², so the triangle is acute scalene triangle.
For the fourth trianlge: A(-3, 1), B(-3, 4), C(-1, 1).
We have
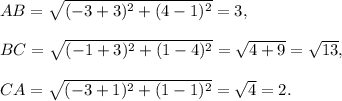
Since AB ≠ BC ≠ CA and BC² + CA² = AB², so the triangle is scalene right-angled triangle.
For the fifth trianlge: A(-4, 2), B(-2, 4), C(-1, 4).
We have
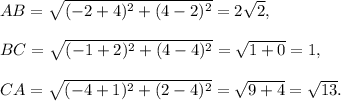
Since AB ≠ BC ≠ CA and AB² + BC² < AB², so the triangle is scalene obtuse-angled triangle.
Thus, the correct match is
A(2, 0), B(3, 2), C(5, 1) isosceles right-angled triangle.
A(4, 2), B(6, 2), C(5, 3.73) isosceles acute angled triangle.
A(-5, 2), B(-4, 4), C(-2, 2) acute scalene triangle.
A(-3, 1), B(-3, 4), C(-1, 1) scalene right-angled triangle.
A(-4, 2), B(-2, 4), C(-1, 4) scalene obtuse-angled triangle.