Answer: x = 6
Explanation:
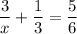
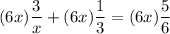 multiplied by common denominator
multiplied by common denominator
18 + 2x = 5x
-2x -2x
18 = 3x
÷3 ÷3
6 = x
Since "x" is in the denominator, the restriction is that x ≠ 0. If the solution was x = 0, then the solution would not be valid and would be eliminated as an answer.
Remember that "x" is just an unknown value. It is possible to add two fractions together and have their sum be a fraction.
For example:
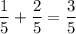 could be written as
could be written as
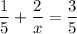 . When we solve it, we will get x = 5.
. When we solve it, we will get x = 5.
******************************************************************************************
Answer: Edward
Explanation:
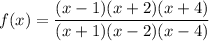
The denominator cannot equal zero, so:
- x + 1 ≠ 0 → x ≠ -1
- x - 2 ≠ 0 → x ≠ 2
- x - 4 ≠ 0 → x ≠ 4
Those x-values are the asymptotes, which is where the function is undefined.