Answer:
1)
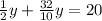 One solution
One solution
2)
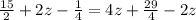 Infinite Number of Solutions
Infinite Number of Solutions
3)
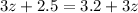 No solution.
No solution.
4)
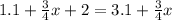 Infinitely Many Solutions
Infinitely Many Solutions
5)
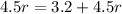 No solution
No solution
6)
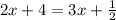 One solution
One solution
Explanation:
Equations may have exactly one solution, uncountable solutions or even no possible solution when the solution is a contradiction and this solution is never true.
1)
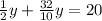 One solution Let's prove it by solving it:
One solution Let's prove it by solving it:
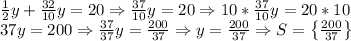
2)
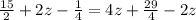 Infinite Number of Solutions because infinitely many solutions satisfies for z.
Infinite Number of Solutions because infinitely many solutions satisfies for z.
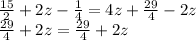
3)
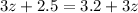 No solution. There's no way to add 2.5 to 3z and have the same amount as adding 3.2 to 3z. This is contradiction. This is a false equality.
No solution. There's no way to add 2.5 to 3z and have the same amount as adding 3.2 to 3z. This is contradiction. This is a false equality.
4)
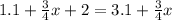 Infinitely many solutions. This equation has infinitely many solutions since the left side is equal to the right side, any value plugged in x may result in many solutions.
Infinitely many solutions. This equation has infinitely many solutions since the left side is equal to the right side, any value plugged in x may result in many solutions.
5)
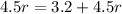 No solution Similarly, again. There's no way of adding 3.2 to 4.5r being equal to 4.5r. Another contradiction. This is a false equality.
No solution Similarly, again. There's no way of adding 3.2 to 4.5r being equal to 4.5r. Another contradiction. This is a false equality.
6)
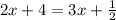 One solution
One solution
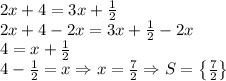
Since we can see on the left side different expressions than on the right side. All that is left is doing the test, by solving it.