Answer:
2.0 J
Step-by-step explanation:
Since the surface is frictionless, we can solve the problem by using the work-energy theorem, which states that the work done on the toy is equal to the kinetic energy gained by the toy:
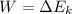
where
W is the work done on the toy
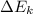 is the kinetic energy gained by the toy
is the kinetic energy gained by the toy
The work done can be calculated as the product between the force applied on the toy and its displacement, so:
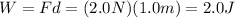
Therefore, according to the work-energy theorem, the toy has gained 2.0 J of kinetic energy.