Answer: Rate law=
![k[A]^1[B]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/n55nfcwdvh18enfrllpccwrgr2496ir98k.png) , order with respect to A is 1, order with respect to B is 2 and total order is 3. Rate law constant is
, order with respect to A is 1, order with respect to B is 2 and total order is 3. Rate law constant is
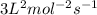
Explanation: Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
![Rate=k[A]^x[B]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/nb363n9puy7up25mzrsrec788uk0kmg0rk.png)
k= rate constant
x = order with respect to A
y = order with respect to A
n = x+y = Total order
a) From trial 1:
![1.2* 10^(-2)=k[0.10]^x[0.20]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/gj24jjmx29iucm407nlj211oyjvem53ryj.png) (1)
(1)
From trial 2:
![4.8* 10^(-2)=k[0.10]^x[0.40]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/n8ckhdw2l2x43bel2mq8i7d5dad5xccew7.png) (2)
(2)
Dividing 2 by 1 :
![(4.8* 10^(-2))/(1.2* 10^(-2))=(k[0.10]^x[0.40]^y)/(k[0.10]^x[0.20]^y)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/qh3vh9uj6j6jkax1yvwxl8vyct1ngpn1l9.png)
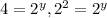 therefore y=2.
therefore y=2.
b) From trial 2:
![4.8* 10^(-2)=k[0.10]^x[0.40]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/n8ckhdw2l2x43bel2mq8i7d5dad5xccew7.png) (3)
(3)
From trial 3:
![9.6* 10^(-2)=k[0.20]^x[0.40]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/efnzou98m2rlhacv9hw4gaqcoekeqjpje3.png) (4)
(4)
Dividing 4 by 3:
![(9.6* 10^(-2))/(4.8* 10^(-2))=(k[0.20]^x[0.40]^y)/(k[0.10]^x[0.40]^y)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/3usg7adl7p17zspapsdvrew6z62s13uc8m.png)
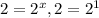 , x=1
, x=1
Thus rate law is
![Rate=k[A]^1[B]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/p62kppgacrxyuoudilcfxk3a2t2veytrfd.png)
Thus order with respect to A is 1 , order with respect to B is 2 and total order is 1+2=3.
c) For calculating k:
Using trial 1:
![1.2* 10^(-2)=k[0.10]^1[0.20]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/qn3k2d6sbrp09bx1tw2umevfduv307dpsl.png)
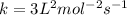 .
.