Answer :
Part (a) :
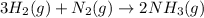
Part (b) : Theoretical yield of
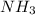 = 440.96 g
= 440.96 g
Part (c) : Percentage yield of ammonia is 90.03 %
Mass of
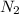 = 475 g
= 475 g
Molar mass of
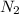 = 28 g/mole
= 28 g/mole
Molar mass of
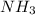 = 17 g/mole
= 17 g/mole
Experimental yield of
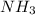 = 397 g
= 397 g
Part (a) :The balanced chemical reaction will be:
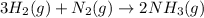
Part (b) :To calculate the moles of
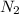 :
:
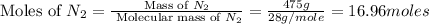
From the given balanced equation:
1 mole of
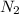 gas produces 2 moles of
gas produces 2 moles of
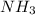
16.96 moles of
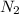 gas produces
gas produces
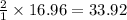 moles of
moles of
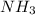
Now we have to calculate the mass of
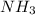
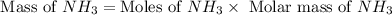
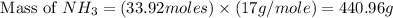
Therefore, the theoretical yield of
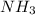 gas = 440.96 g
gas = 440.96 g
Part (c) : Percentage yield :
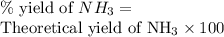
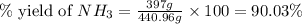
Therefore, the % yield of ammonia is 90.03 %