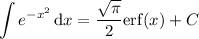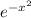 has no antiderivative in terms of elementary functions (polynomials, exponentials, logarithms, trigonometric functions, etc), but there is a special function defined to fit that role called the error function,
has no antiderivative in terms of elementary functions (polynomials, exponentials, logarithms, trigonometric functions, etc), but there is a special function defined to fit that role called the error function,
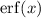 , where
, where
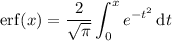
By the fundamental theorem of calculus, we can see that
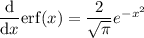
which means we have