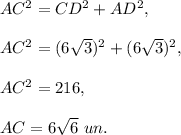Answer:
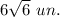
Explanation:
Consider right triangle ABC with right angle ACB. If m∠ACD = 45°, then
m∠BCD=m∠ACB-m∠ACD=90°-45°=45°.
Since CD ⊥ AB, then
m∠CDA=m∠CDB=90°.
Thus, triangles ACD and BCD are right triangles with right angles ADC and BDC. In these triangles:
m∠CAD=90°-m∠ACD=90°-45°=45°;
m∠CBD=90°-m∠BCD=90°-45°=45°.
Thus, triangles ACD and BCD are isosceles right triangles with
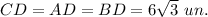
By the Pythagorean theorem,