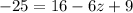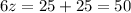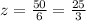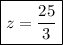Answer:
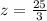
Explanation:
Pythagora's Theorem
In any right triangle, the square of the measure of the hypotenuse is the sum of the squares of the legs. This can be expressed with the formula:
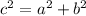
Where
c = Hypotenuse or largest side
a,b = Legs or shorter sides
We are required to find z in the figure provided. We have completed the construction with two additional variables h and x in the image below.
The triangle to the left side has hypotenuse 5 and one leg of 3, thus:
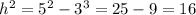
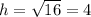
Now for the bigger triangle:
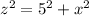
Solving for
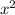
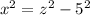
For the smaller right-side triangle:
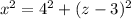
Equating both equations:
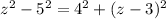
Expanding the square:
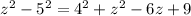
Simplifying and operating: