Answer:
55.0 g/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1. Partial pressure of hydrogen
You are collecting the gas over water, so
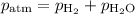

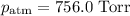
At 25 °C,
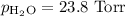
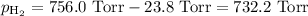
===============
Step 2. Moles of H₂
We can use the Ideal Gas Law.
pV = nRT Divide both sides by RT
n = (pV)/(RT)
p = 732.2 Torr Convert to atmospheres
p = 732.2/760
p = 0.9634 atm
V = 291 mL Convert to litres
V = 0.291 L
R = 0.082 06 L·atm·K⁻¹mol⁻¹
T = 25 °C Convert to kelvins
T = (25 + 273.15 ) K = 298.15 K
n = (0.9632 × 0.291)/(0.082 06 × 298.15)
n = 0.2804/24.47
n = 0.011 46 mol
===============
Step 3. Moles of metal
The partial chemical equation is
M + H₂SO₄ ⟶ H₂ + …
The molar ratio of M:H₂ is 1 mol M:1 mol H₂.
Moles of M = 0.011 46× 1/1
Moles of M = 0.011 46 mol M
===============
Step 4. Atomic mass of M
Atomic mass = mass of M/moles of M
Atomic mass = 0.630/0.011 46
Atomic mass = 55.0 g/mol