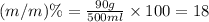Answer : The concentration can be expressed as, 1.99 M, or 15.1(m/m)%, or 18(m/v)%
Solution : Given,
Volume of solution = 0.5 L = 500 ml (1 L = 1000 ml)
Mass of solution = 596 g
Mass of oxalic acid, (solute) = 90 g
Molar mass of oxalic acid = 90.03 g/mole
First we have to calculate the concentration in terms of M(molarity).
Molarity : Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute present in one liter of solution.
Formula used :
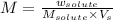
where,
M = molarity of solution
 = mass of solute(oxalic acid)
= mass of solute(oxalic acid)
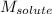 = molar mass of solute(oxalic acid)
= molar mass of solute(oxalic acid)
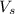 = volume of solution(in liters)
= volume of solution(in liters)
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get
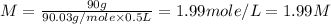
Now we have to calculate the concentration in terms of (m/m)%
(m/m)% : It is defined as the mass of solute present in mass of solution in grams.
Formula used :
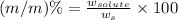
where,
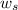 = mass of solution
= mass of solution
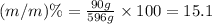
Now we have to calculate the concentration in terms of (m/v)%
(m/v)% : It is defined as the mass of solute present in one milliliter of solution.
Formula used :
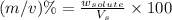
where,
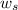 = mass of solution
= mass of solution