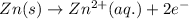Answer: The half reaction occurring at anode is
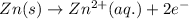
Step-by-step explanation:
In a chemical cell, substance getting oxidized always act as anode and the one getting reduced always act as cathode.
Oxidation reaction is defined as the reaction in which an atom looses its electrons. Here, oxidation state of the atom increases.
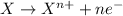
Reduction reaction is defined as the reaction in which an atom gains electrons. Here, the oxidation state of the atom decreases.
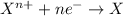
For the given chemical cell reaction:
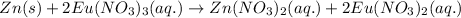
Oxidation half reaction (anode):
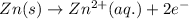
Reduction half reaction (cathode):
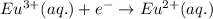 ( × 2 )
( × 2 )
Here, zinc is loosing electrons and is getting oxidized and europium is gaining electrons and loosing electrons.
Hence, the half reaction occurring at anode is