Answer : The reactant acid and conjugate base in this reaction is,
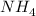 and
and
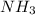 .
.
Explanation :
Conjugate acid : A species that is formed by receiving of a proton
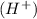 by a base is known as conjugate acid.
by a base is known as conjugate acid.
Conjugate base : A species that is formed by donating of a proton by an acid is known as conjugate base.
The given chemical reaction is,
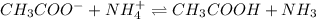
In this reaction,
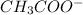 (base) react with
(base) react with
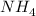 (acid) to give
(acid) to give
 (conjugate acid) and
(conjugate acid) and
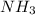 (conjugate base).
(conjugate base).
Therefore, the reactant acid and conjugate base in this reaction is,
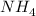 and
and
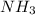 .
.