Event A Answer:
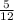
Explanation:
sum greater than 7 leaves are the following combinations for 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12:
8 = 26, 35, 44, 51, 62 (5 possibilities)
9 = 36, 45, 54, 63 (4 possibilities)
10 = 46, 55, 64 (3 possibilities)
11 = 56, 65 (2 possibilities)
12 = 66 (1 possibility)
This is a total of 15 possibilities out of 36 total:
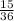 =
=
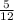
***********************************************************************************
Event B Answer:

Explanation:
sum is an even number means both dice are odd or both dice are even. That results in the following combinations:
11 13 15
22 24 26
31 33 35
42 44 46
51 53 55
62 64 66
This is a total of 18 possibilities out of 36 total:
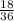 =
=
