Answer:
0.14 s
Explanation:
s = -2.7 t² + 40t + 6.5
Let s = 12
12 = -2.7t² + 40t + 6.5 Subtract 12 from each side
-2.7t² + 40t + 6.5 - 12 = 0
-2.7t² + 40t - 5.5 = 0
Apply the quadratic formula
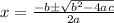
a = -2.7; b = 40; c = -5.5
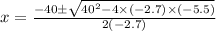
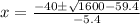
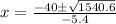
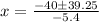
x = 7.41 ± 7.27
x₁ = 0.14; x₂ = 14.68
The graph below shows the roots at x₁ = 0.134 and x₂ = 14.68.
The Moon’s surface is at -12 ft. The ball will be 12 ft above the Moon’s surface (crossing the x-axis) in 0.14 s.
The second root gives the time the ball will be 12 ft above the Moon’s surface on its way back down.