Answer:
Original claim is
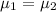
Opposite claim is
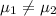
Null and alternative hypotheses:
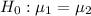
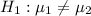
Significance level: 0.01
Test statistic:
We can use TI-84 calculator to find the test statistic and P-value. The steps are as follows:
Press STAT and the scroll right to TESTS
Scroll down to 2-SampTTest... and scroll to stats.
Enter below information.
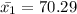
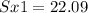
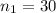
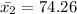
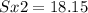
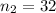
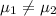
Pooled: Yes
Calculate.
The output is in the attachment.
Therefore, the test statistic is:
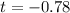
P-value: 0.4412
Reject or fail to reject: Fail to reject
Final Conclusion: Since the p-value is greater than the significance level, we, therefore, fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the there is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the samples are from populations with the same mean.