Answer:
![[HI] _(eq)=0.825mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/3m8bm8mqggpivgclwjoqbsvf8g6lfpuqjw.png)
![[H_2] _(eq)=0.010mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/xjzf7v4d7e5410barddplpt08dru4zlz8i.png)
![[I_2] _(eq)=0.078mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/xcqxawg3hpppc2kn5bhfb2vs8et4gmgmx2.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
At first, the undergoing chemical reaction is:
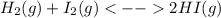
So the law of mass action in terms of concentration turns out into (remember the relationship between Kp and K
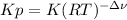 ):
):
![(Kp)/((RT)^(2-2) )=([HI]^(2)_(eq) )/([H_2]_(eq)[I_2]_(eq)) \\Kp=([HI]^(2)_(eq) )/([H_2]_(eq)[I_2]_(eq))](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/2i7zovjuwlg475dvxhmjrmu16mxhaa83ig.png)
Now, we need the initial concentrations which are computed by knowing the volume computed with the ideal gas equation with the total initial moles:
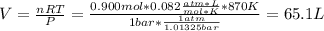
Thus,
![[H_2] _0=(0.300mol)/(65.1L)=0.005M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/qylv5czkegdpinevl603v0bzb5jxncz4pt.png)
![[I_2] _0=(0.400mol)/(65.1L)=0.006M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/l2z3jfw4ftcr7ohss3sbpjhbwhmlupxspy.png)
![[HI] _0=(0.200mol)/(65.1L)=0.003M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/yozwxbqofwlqhue5ok77kw2ugsj235ex9q.png)
Thus, by considering the change, we write the law of mass action in terms of the change
 due to the equilibrium:
due to the equilibrium:
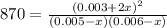
Solving for
 we obtain:
we obtain:
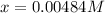
Thus, the amounts turn out into:
![[HI] _(eq) =(0.003M +2(0.00484M))*65.1L=0.825mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/g0kbdzitk6k74gf5qwkutova12zopk7yvk.png)
![[H_2] _(eq) =(0.005M -0.00484M)*65.1L=0.010mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/dsxlshkzzk49lb4d6cax7qux3ppyatlkir.png)
![[I_2] _(eq) =(0.006M -0.00484M)*65.1L=0.078mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/p8craeewlkun4przre2agzkhmhni7tme27.png)
Best regards.