Answer:
Critical value f(1)=2.
Minimum at (1,2), function is decreasing for
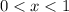 and increasing for
and increasing for
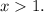
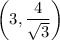 is point of inflection.
is point of inflection.
When 0<x<3, function is concave upwards and when x>3, , function is concave downwards.
Explanation:
1. Find the domain of the function f(x):
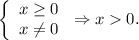
2. Find the derivative f'(x):
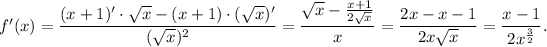
This derivative is equal to 0 at x=1 and is not defined at x=0. Since x=0 is not a point from the domain, the crititcal point is only x=1. The critical value is
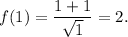
2. For
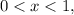 the derivative f'(x)<0, then the function is decreasing. For
the derivative f'(x)<0, then the function is decreasing. For
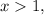 the derivative f'(x)>0, then the function is increasing. This means that point x=1 is point of minimum.
the derivative f'(x)>0, then the function is increasing. This means that point x=1 is point of minimum.
3. Find f''(x):
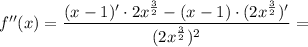
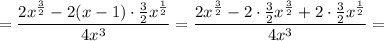
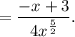
When f''(x)=0, x=3 and
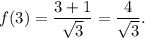
When 0<x<3, f''(x)>0 - function is concave upwards and when x>3, f''(x)>0 - function is concave downwards.
Point
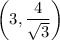 is point of inflection.
is point of inflection.