Step-by-step explanation:
Elevation of boiling point :
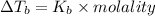
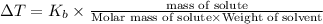
From the above expression we can say that :

Increasing the mass of the solute in a solution will increase the concentration of the solute in a solution by which the value
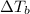 will also get increased and vice-versa.
will also get increased and vice-versa.
Increased in value of
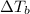 means that boiling point of solution will also get increased.
means that boiling point of solution will also get increased.
So, increase in concentration of solute in solution will increase the boiling point of the solution and vice-versa
Depression in freezing point:
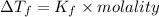
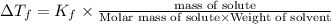
From the above expression we can say that :
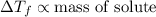
Increasing the mass of the solute in a solution will increase the concentration of the solute in a solution by which value
 will also get increased and vice-versa.
will also get increased and vice-versa.
Increased in value of
 means that freezing point of solution will also get increased which means that more lowering in freezing point will take place.
means that freezing point of solution will also get increased which means that more lowering in freezing point will take place.
So, increase in concentration of solute in solution will increase the lowering in freezing point of the solution and vice-versa