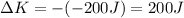Answer:
200 J
Step-by-step explanation:
By the law of conservation of energy, the kinetic energy gained by the object during the fall is equal to the loss of gravitational potential energy:
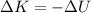
The loss of gravitational potential energy of the object over a distance of 10 m is given by:
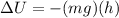
where
(mg) = 20 N is the weight of the object
h = 10 m is the loss in height
Substituting, we find
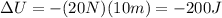
So, the kinetic energy gained by the object is