Answer:
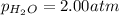
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, according to the following chemical reaction:
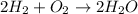
It means that we need to compute the moles of hydrogen and oxygen that are reacting, via the ideal gas equation as we know the volume, pressure and temperature:
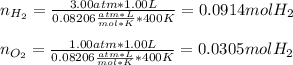
Thus, the yielded moles of water are computed by firstly identifying the limiting reactant:
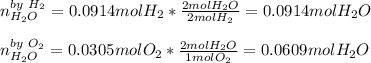
Thus, the fewest moles of water are 0.0609 mol so the limiting reactant is oxygen; in such a way, by using the ideal gas equation once again, we compute the pressure of water:
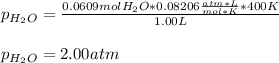
Best regards!