Answer:
ΔQ = 5054 KJ/kg.K
Step-by-step explanation:
First of all, we will find the value of the specific heat of hydrogen. Since it is mentioned that the value of specific heat is constant between 300 K and 650 K. Therefore, we can take it to be the average of values at these two temperatures.
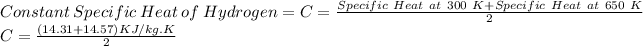 C = 14.44 KJ/ kg.K
C = 14.44 KJ/ kg.K
Now, the heat absorbed is given by the following formula:
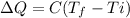
where,
T_f = Final Temperature = 650 K
T_i = Initial Temperature = 300 K
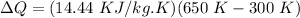
ΔQ = 5054 KJ/ kg.K