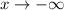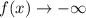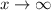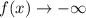Answer:
A: Nature of root
we have a formula to find the roots of quadratic equation
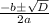
where,
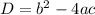
We have general form of quadratic equation as
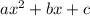
Here, a=-3,b=6 and c=17 on substituting the values in
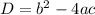 and
and
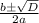
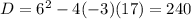
Now, substitute D we get
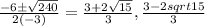
B: Open upward or downward
This given function is a downward parabola you can refer the figure in the attachment
C: End behaviour
Here, we have negative leading coefficient and even degree
Hence,