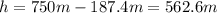1. Velocity at which the packet reaches the ground: 121.2 m/s
The motion of the packet is a uniformly accelerated motion, with constant acceleration
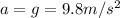 directed downward, initial vertical position
directed downward, initial vertical position
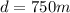 , and initial vertical velocity
, and initial vertical velocity
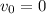 . We can use the following SUVAT equation to find the final velocity of the packet after travelling for d=750 m:
. We can use the following SUVAT equation to find the final velocity of the packet after travelling for d=750 m:
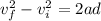
substituting, we find
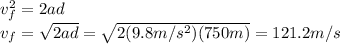
2. height at which the packet has half this velocity: 562.6 m
We need to find the heigth at which the packet has a velocity of
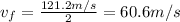
In order to do that, we use again the same SUVAT equation substituting
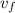 with this value, so that we find the new distance d that the packet travelled from the helicopter to reach this velocity:
with this value, so that we find the new distance d that the packet travelled from the helicopter to reach this velocity:
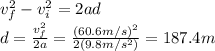
Which means that the heigth of the packet was